Hashgraph
While not actually a blockchain at all Hashgraph, like blockchain, is based on Distributed Ledger technology (DLT) and is often referred to as the 3rd generation of Distributed Ledgers and a natural progression from blockchain, hence why it is included on this site. Founded in 2018 and created by Leemon Baird, Hashgraph has come as an alternative to blockchain and is aimed at enterprise use.
A major difference between blockchain and Hashgraph is how they structure their ledgers. In both, when a transaction is made, the information of that transaction is put into a container and spread throughout the distributed network. In blockchain, the container is the “blocks” and they are intended to form a single, long chain. In some situations, two blocks can be created at the same time, the network nodes will eventually choose one chain to continue and discard the other one. It is comparable to constantly pruning a growing tree.
In Hashgraph, every container is incorporated into the ledger, meaning none are discarded. All the branches continue to exist forever and are woven together into a single whole. Because of this, Hashgraph is much more efficient than blockchain. This also allows for better scalability and a higher level of security than attainable by blockchain known as “Byzantine Fault Tolerant” (BFT).
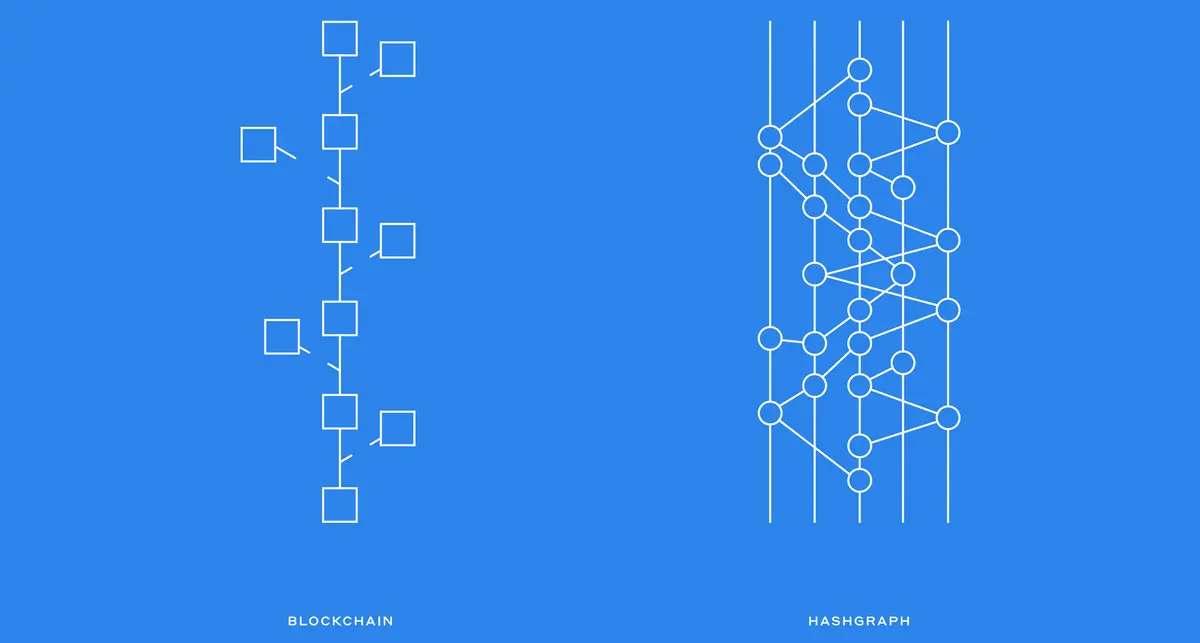
Another major difference between blockchain and Hashgraph is that the blockchain project is open source while Hashgraph is a currently patented technology. Hashgraph is promising, but currently it has only been deployed in private and permission-based networks. It is still to be tested and explored in a public network.

 Blockchain 360
Blockchain 360